Molecule Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v1.26, by Herong Yang
Genetic Transcription - Creating mRNA
This section provides a quick introduction of the Genetic Transcription process, which is the process of copying genetic information of a gene from DNA to a special RNA molecule called mRNA (Messenger RNA).
What Is Genetic Transcription? - Genetic Transcription is the process of copying genetic information of a gene from DNA to a special RNA molecule called mRNA (Messenger RNA). Transcription is the first step in the expression process from gene to protein.
The genetic transcription process can be divided into 3 phases, initiation, elongation and termination.
1. Initiation Phase - During the initiation phase, a special enzyme called RNA polymerase recognizes a specific site on the DNA, upstream from the gene that will be transcribed, called a promoter site and then unwinds the DNA locally.
2. Elongation Phase - During the Elongation phase, the RNA polymerase uses the antisense (-) strand of gene as the template and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule called mRNA (Messenger RNA).
3. Termination Phase - When the RNA polymerase reaches the STOP codon of the gene, it will stop transcription, release the newly created mRNA and dissociate itself from the gene.
The picture (source: microbenotes.com) below illustrates the Genetic Transcription process and its 3 phases:
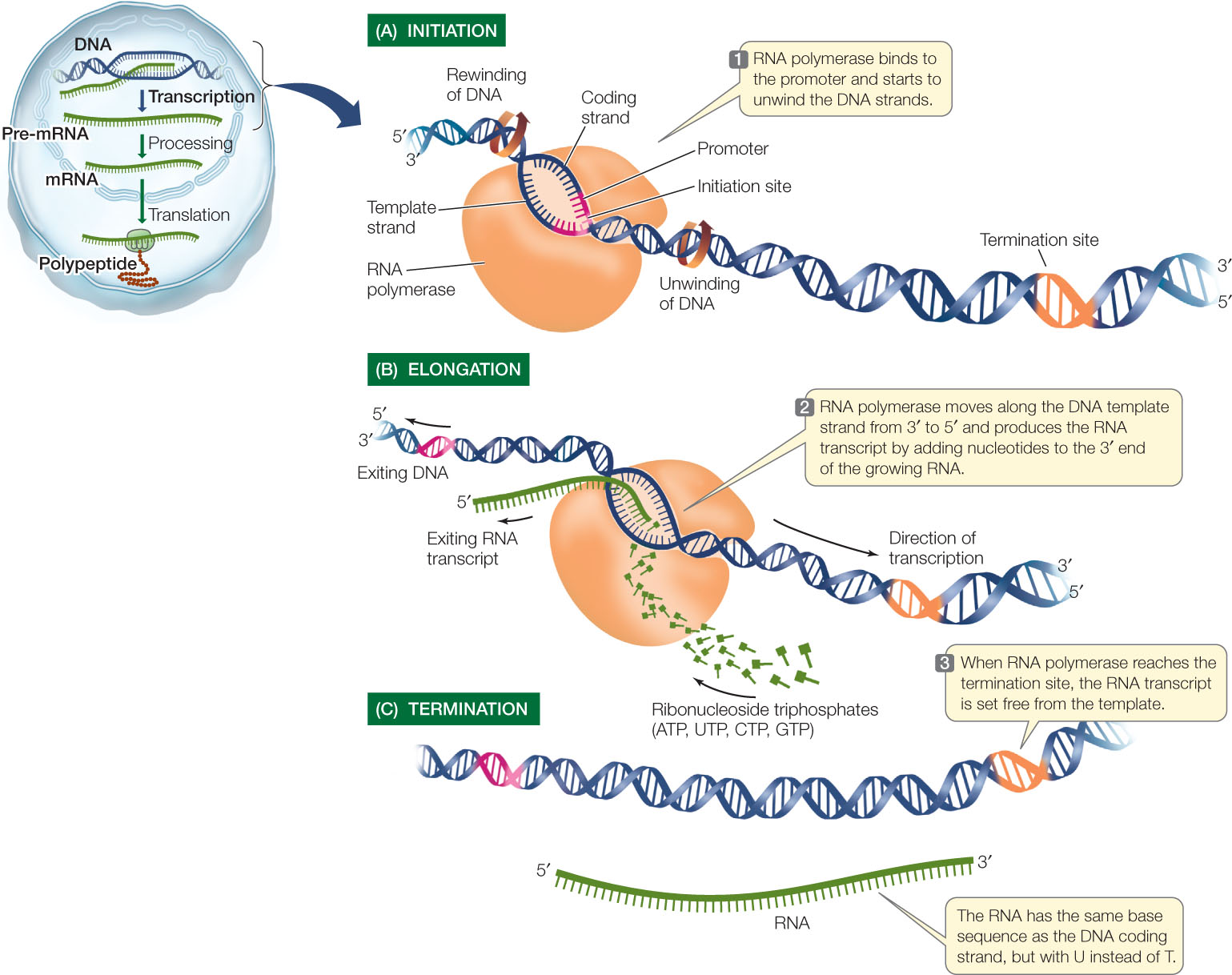
Since the mRNA is complementary to the antisense strand of the gene, so it is identical to the sense strand of the gene. In other words, the mRNA has the same instruction codons as the gene, except that Nucleotide U (Uridine) is used in mRNA instead of T (Thymidine).
Once the draft mRNA is created, it will go through some minor changes of splicing, capping and tailing to become the final mRNA.
The final mRNA will then escape from the cell nucleus to serve as a genetic template to build new proteins during the translation process.
Table of Contents
Molecule Names and Identifications
Nucleobase, Nucleoside, Nucleotide, DNA and RNA
Gene Expression - Building Proteins
►Genetic Transcription - Creating mRNA
Genetic Translation - Creating Protein
DNA Gene Sequence - Exons and Introns
Chromosome Replication (or DNA Replication)
ChEMBL Database - European Molecular Biology Laboratory
PubChem Database - National Library of Medicine
INSDC (International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration)
HGNC (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee)