PKI Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - Version 2.04, by Dr. Herong Yang
Deleting Root CA Certificates from Chrome 40
This section provides a tutorial example on how to delete a certificate from Chrome 40. Deleted certificate can be re-installed back from a certificate file.
As you can see from the previous tutorial, the list of trusted root CA certificates in Chrome is quite long. It contains many root CA certificates you are probably never going to use them. If you want to, you can delete root CA certificates that are not needed from Chrome 40.
Here is what I did on Chrome 40 to delete the "VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5" certificate, which is actually needed to validate the login.yahoo.com certificate. But I can delete it, because I have exported it to a file already.
1. Click "Start > All programs > Google Chrome".
2. Right-mouse click "Google Chrome", then select "Run as administrator" to start Chrome. Running Chrome as administrator gives you the permission to remove root certificate.
3. Go to the "Settings" after click the menu icon on top right corner. You see the settings page showing up.
4. Click the "Show advanced settings..." link at the bottom.
5. Click the "Manage certificates..." button in the HTTPS/SSL section. You see Certificates manager showing up.
6. Go to the "Trusted Root Certificate Authorities" tab and select "VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5".
7. Click the "Remove" button, A warning message box shows up:
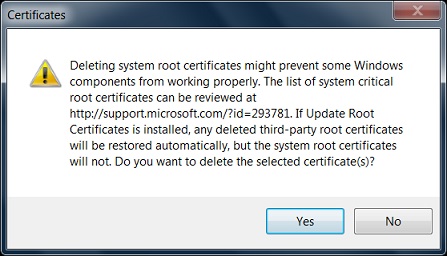
8. Read the warning message and click "OK":
Deleting system root certificate might prevent some Windows components from working properly. ... If Update Root Certificates is installed, any deleted third-party root certificates will be restored automatically, but the system root certificates will not. Do you want to delete the selected certificate(s)?
9. Close Chrome 40.
The "VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority - G5" certificate is deleted from Chrome 40 now.
Last update: 2015.
Table of Contents
Introduction of PKI (Public Key Infrastructure)
Introduction of HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
Using HTTPS with IE (Internet Explorer) 10
Visiting "https" Web Site with Chrome 40
Viewing Server Certificate in Chrome 40
Viewing Server Certificate Path in Chrome 40
Exporting Server Certificate to File in Chrome 40
Viewing Trusted Root CA Certificates in Chrome 40
Listing of Trusted Root CA in Chrome 40
Exporting Root Certificate to File from Chrome 40
►Deleting Root CA Certificates from Chrome 40
Chrome 40 Shares Windows PKI with IE
Perl Scripts Communicating with HTTPS Servers
PHP Scripts Communicating with HTTPS Servers
Java Programs Communicating with HTTPS Servers
Certificate Stores and Certificate Console
.NET Programs Communicating with HTTPS Servers
CAcert.org - Root CA Offering Free Certificates
PKI CA Administration - Issuing Certificates
Digital Signature - Microsoft Word 2007
Digital Signature - OpenOffice.org 3