Physics Notes - Herong's Tutorial Notes - v3.24, by Herong Yang
What Is Speed
This section provides a quick introduction of speed, which is a derived property of a moving object by calculating the distance the object has moved within a single unit of time.
What Is Speed? Speed is a derived property of a moving object by calculating the distance the object has moved within a single unit of time.
The speed of a moving object can be expressed as a formula: v = d/t, where v represents the speed, d represents the distance the object has moved, and t represents the duration of time. The standard units of measure used in this formula are:
v (speed): meter per second (m/s) d (distance): meter (m) t (time): second (s)
For example, to calculate the speed of a running athlete, we can use the following process:
- Mark the starting location as A and the ending location as B.
- Set the x-axis coordinate along the track with the origin point at A.
- Record the time from a clock as t1 (0 s) when the athlete pass the location A.
- Record the time from the same clock as t2 (5 s) when the athlete pass the location B.
- Take the coordinate of A as d1 (0 m).
- Take the coordinate of B as d1 (50 m).
- Calculate the distance between A and B: d = d2 - d1 = 50 m.
- Calculate the duration used by the athlete: t = t2 - t1 = 5 s.
- Calculate the speed of the athlete: v = d/t = 10 m/s.
So the speed of the running athlete is v = 10 m/s.
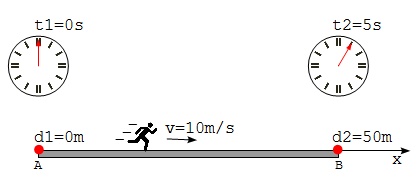
Table of Contents
Introduction of Frame of Reference
Different Speeds Observed in Different Frames
Measuring Speed of Light - Roemer's Method
Measuring Speed of Light - Fizeau's Method
Measuring Speed of Light - Foucault's Method
Introduction of Special Relativity
Time Dilation in Special Relativity
Length Contraction in Special Relativity
The Relativity of Simultaneity
Minkowski Spacetime and Diagrams
Introduction of Generalized Coordinates